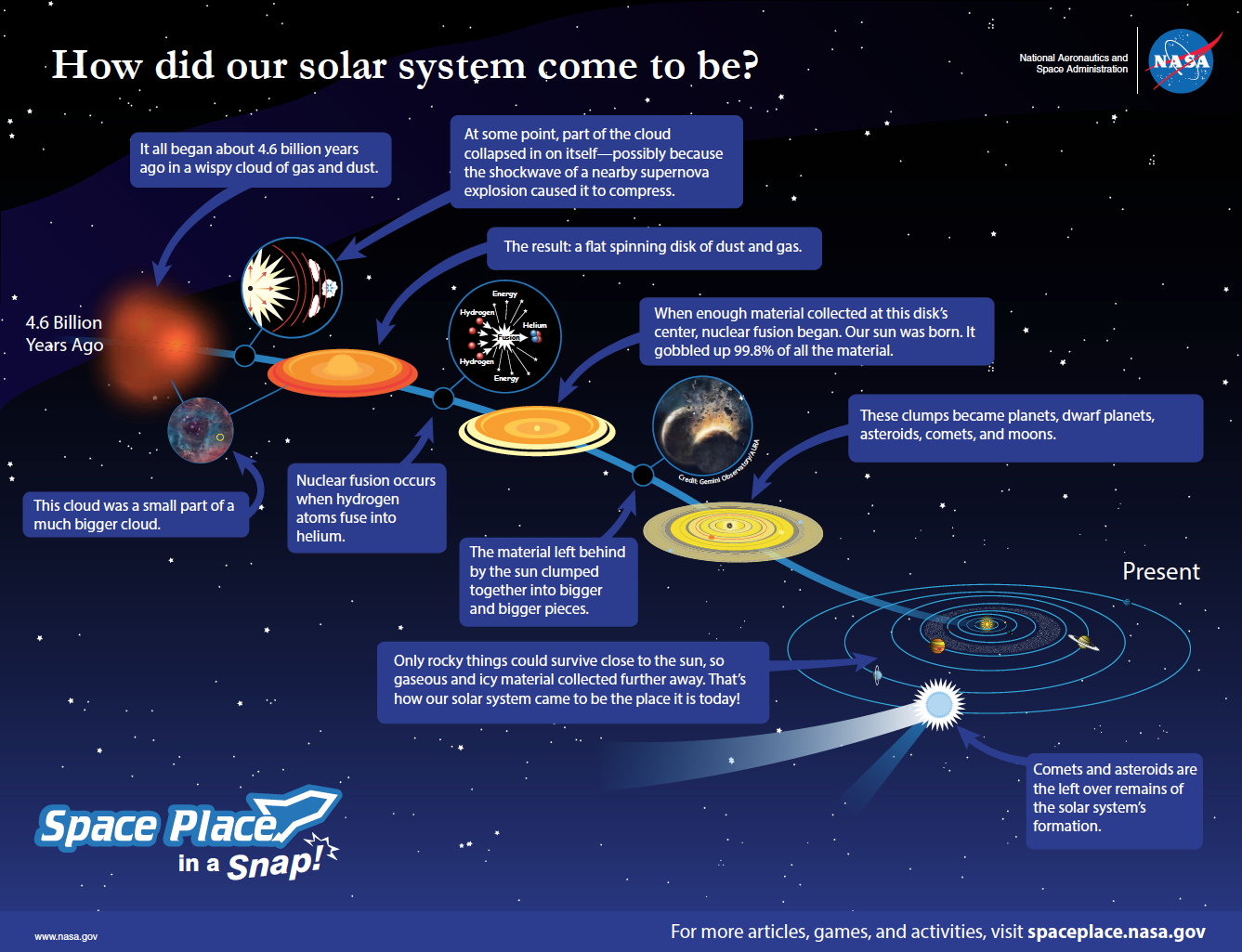
Approximately 4.6 billion years ago, our solar system was a cloud of dust and gas known as the solar nebula. As gravity caused the material to collapse in on itself, it spun faster and faster and eventually flattened into a disk. Researchers believe that most of the material accumulated in the center, to form the sun, while the rest clumped together, creating protoplanets – balls of gas, dust, and rocks, about the size of Mercury or Mars. Over the years, some of the protoplanets collided to form our eight planets, while the rest continue to whirl around the sun as asteroids or rocky debris. However, the one thing scientists are not sure is the process by which the planets came together. Now, a 4.565 billion-year-old space rock, the oldest igneous meteorite ever discovered, may provide clues to this age-old mystery.